Introduction
The insurance sector’s finance function is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the convergence of advanced technologies, data analytics, and automation. As the industry navigates an increasingly complex regulatory environment, rising customer expectations, and rapid market changes, insurance Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) are stepping into strategic roles. They are spearheading initiatives to modernize finance functions, ensuring compliance and operational efficiency and positioning their organizations for sustained growth in a dynamic business environment.
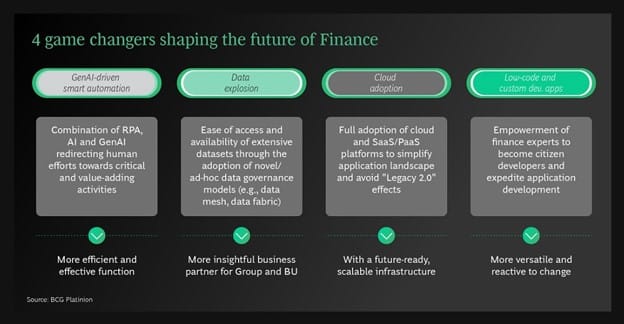
This transformation is underpinned by several key technological and operational shifts, including integrating Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI), cloud computing, advanced data governance frameworks, and low-code/no-code platforms. Together, these advancements enable CFOs to elevate their contributions from traditional financial stewardship to proactive business leadership. By leveraging these innovations, CFOs are redefining the role of finance within their organizations, transforming it into a strategic partner that drives agility, innovation, and resilience.
Generative AI and Automation
Transforming Specialized Finance Functions
Generative AI is rapidly emerging as a game-changer in the insurance sector, particularly within specialized finance functions such as actuarial reserving, financial hedging, and risk management. These areas traditionally involve complex computations, heavy reliance on historical data, and significant manual intervention—all of which are ripe for disruption through automation and AI.
Automating Actuarial Reserving
Actuarial reserving, a cornerstone of insurance finance, involves estimating future liabilities to ensure that insurers have sufficient reserves to meet policyholder obligations. This process, while critical, is often time-consuming and prone to errors due to the complexity of the underlying calculations and the sheer volume of data involved.
Generative AI models are revolutionizing this process by analyzing vast datasets—including historical claims data, macroeconomic indicators, and market trends—to predict future liabilities with unprecedented accuracy. These models employ advanced machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and correlations that might be missed by traditional actuarial methods. For instance, an AI model could detect emerging risks in real-time, such as the financial implications of climate change on property insurance claims, enabling insurers to adjust their reserving strategies accordingly.
Optimizing Financial Hedging
In financial hedging, AI-driven algorithms are being deployed to assess market conditions and optimize hedging strategies. By analyzing real-time data, such as interest rate movements, currency fluctuations, and commodity prices, these algorithms can recommend precise hedging actions that minimize risk exposure while maximizing returns. This level of optimization not only enhances financial performance but also provides CFOs with actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Moreover, automating these functions with GenAI reduces manual intervention, minimizing the risk of human errors and accelerating the decision-making process. By standardizing workflows and eliminating redundancies, organizations can enhance the efficiency of core finance operations by as much as 20%, freeing up resources to focus on higher-value strategic activities.
Data Explosion and Governance
Turning Challenges into Opportunities
The exponential growth of data in the insurance industry presents a double-edged sword. While the availability of vast amounts of data offers unparalleled opportunities for insights and innovation, it also poses significant challenges in terms of data management, quality, and security.
Harnessing Data as a Strategic Asset
CFOs are increasingly taking on the role of data architects, responsible for designing and implementing robust data governance frameworks. These frameworks often include centralized data architectures, such as data lakes and service meshes, which enable organizations to unify data from diverse internal and external sources. For example, data lakes allow insurers to consolidate structured data (e.g., financial transactions) and unstructured data (e.g., customer feedback) into a single repository, making it easier to derive actionable insights.
By leveraging advanced analytics and visualization tools, CFOs can transform raw data into meaningful insights that drive informed decision-making. For instance, predictive analytics can help insurers identify high-risk customer segments. While real-time analytics can provide actionable insights into operational performance.
Ensuring Data Quality and Compliance
Effective data governance is critical for ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and security of data. This is particularly important in the insurance industry, where compliance with stringent regulatory requirements—such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Solvency II—is non-negotiable.
By establishing clear data ownership and accountability, implementing robust data quality controls, and employing advanced encryption technologies. CFOs can mitigate risks associated with data breaches and regulatory non-compliance. Moreover, a strong data governance framework builds stakeholder trust Positioning data as a strategic asset that drives innovation and competitive advantage.
Cloud Infrastructure
Enabling Agility and Scalability
The adoption of cloud infrastructure is a pivotal step in modernizing insurance finance functions. Cloud computing offers the agility and scalability needed to respond to real-time market changes, regulatory demands, and evolving customer expectations.
Reducing IT Complexity
Migrating finance operations to the cloud simplifies IT infrastructure, reducing complexity and operational costs. Cloud platforms provide scalable resources that can be adjusted based on demand, ensuring that finance operations remain resilient during peak periods, such as financial reporting cycles or regulatory audits.
For example, a cloud-based financial planning and analysis (FP&A) system can enable real-time collaboration across geographically dispersed teams, improving efficiency and accuracy. Similarly, cloud-based platforms support advanced analytics and machine learning applications, enabling CFOs to derive actionable insights from large datasets.
Supporting Innovation
The cloud also facilitates faster, more cost-effective innovation. By providing a flexible and scalable environment, cloud platforms enable insurance companies to experiment with new technologies. Such as AI and blockchain, without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware or infrastructure.
Additionally, the cloud’s inherent scalability ensures that finance operations can easily adapt to growth, whether it’s the launch of a new product line or expansion into new markets. This agility is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving insurance landscape.
Low-Code/No-Code Solutions
Empowering Finance Teams
Low-code and no-code platforms are democratizing application development. Enabling finance teams to rapidly create customized tools for data analysis, reporting, and workflow automation without extensive coding knowledge.
Enhancing Operational Agility
By empowering finance professionals to develop and modify applications tailored to their specific needs. Low-code/no-code platforms reduce dependency on IT departments and increase operational adaptability. For example, a finance team could use a low-code platform to develop a dashboard that tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, enabling faster and more informed decision-making.
This agility is particularly valuable in the insurance industry. Where timely access to accurate information is critical for responding to changing market conditions and regulatory requirements.
Reducing Costs and Time-to-Market
Low-code/no-code platforms also reduce development costs and time-to-market for new applications. By providing pre-built templates and drag-and-drop functionality, these platforms enable finance teams to quickly prototype and deploy solutions, improving responsiveness to business needs.
Strategic Implications for CFOs
Shaping the Future of Finance
The convergence of data, automation, and scalable technologies is redefining the role of CFOs in the insurance industry. To remain competitive, CFOs must embrace these advancements and integrate them into their finance functions. By doing so, they can:
1. Enhance Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce operational costs.
2. Drive Innovation: Leverage advanced analytics and AI to uncover new opportunities and optimize decision-making.
3. Foster Resilience: Build agile and scalable finance functions capable of adapting to market and regulatory changes.
4. Strengthen Compliance: Implement robust data governance frameworks to ensure accuracy, consistency, and security.
CFOs who adopt a forward-thinking approach will cultivate lean, responsive finance functions that support their organizations’ strategic objectives. By embracing GenAI, robust data governance, cloud infrastructure, and low-code/no-code solutions. CFOs can not only drive operational excellence but also position their organizations for sustained growth and competitiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intersection of data, automation, and scalability is transforming the finance function in the insurance industry. CFOs equipped with these tools are well-positioned to navigate the complexities of the modern financial landscape. Ensuring that their organizations remain resilient. And competitive in the face of change. The future of insurance finance is not just about managing numbers. It’s about creating value, fostering innovation, and driving strategic success.
References
https://www.bcgplatinion.com/insights/technology-trends-shaping-the-future-of-finance-in-insurance