Organizations have adopted DevOps practices to increase their ability to deliver applications and services at a high velocity. A basic understanding of different AWS services would help identify the preferred service.
What is AWS CodeBuild?
In the cloud, AWS CodeBuild fully manages the build service. AWS CodeBuild compiles the source code, runs unit tests, and produces artifacts that are ready to deploy. CodeBuild eliminates the need to provision, manage, and scale own build servers. It provides prepackaged build environments for popular programming languages and builds tools such as Apache Maven, Gradle, and more. It gives the flexibility to customize build environments in CodeBuild to use own build tools. CodeBuild scales automatically to meet peak build requests.
What is AWS CodePipeline?
It actively manages continuous delivery services, automating release pipelines for swift and dependable updates to applications and infrastructure. CodePipeline automates the build, test, and deploy phases of the release process every time there is a code change, based on the defined release model. This enables rapid and reliable delivery of features and updates. AWS CodePipeline can easily integrate with third-party services such as GitHub or any other custom plugin.
Difference between CodeBuild and CodePipeline
The main difference between the two lies in classifying AWS CodeBuild as a tool in the Continuous Integration category, while AWS CodePipeline falls under Continuous Deployment.
What is Continuous Integration?
Continuous integration is a software development method where members of the team can integrate their work at least once a day. In this method, an automated build checks every integration to detect errors. Continuous integration involves building and testing the software immediately after a code commit. In large projects with numerous developers, commits occur frequently throughout the day. Each commit triggers the building and testing of code. If the tests pass, the build undergoes Deployment testing. Upon successful Deployment, the code is pushed to production. This commit, build, test, and deploy is a continuous process, hence the name continuous integration/deployment.
What is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous delivery is a software engineering method in which a team develops software products in a short cycle. It ensures that software can be easily released at any time.
The main aim of continuous delivery is to build, test, and release software with good speed and frequency. It helps to reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for frequent updates in production.
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous deployment is a software engineering process in which product functionalities are delivered using automatic deployment. It helps testers to validate whether the codebase changes are correct and stable or not.
The team can achieve continuous deployment by relying on infrastructure that automates different testing steps. Once each integration satisfies this release criteria, the application updates with new code.
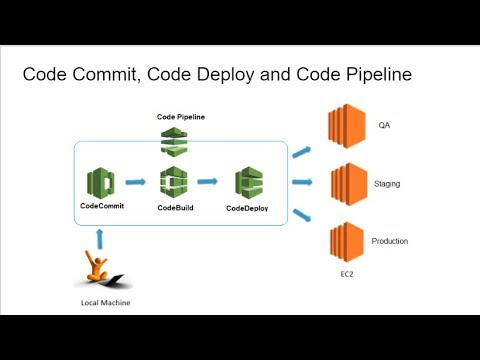
How to run AWS CodeBuild and AWS CodePipeline?
To run the CodeBuild, AWS CodeBuild or AWS CodePipeline console can be used. AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) or the AWS SDKs can also be used to automate the running of CodeBuild.
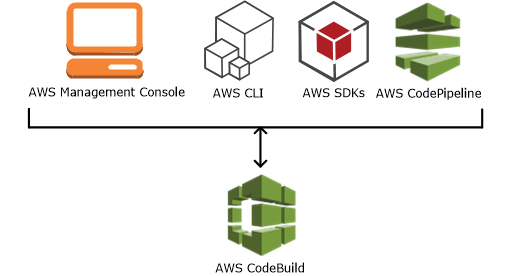
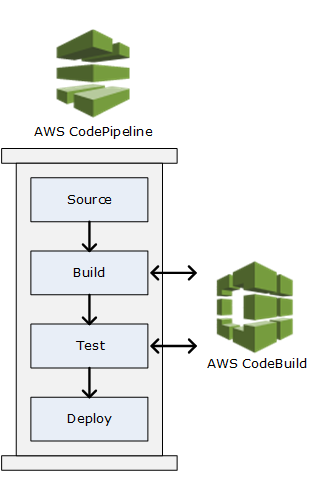
The CodeBuild can then be added as a build or test action to the build or test stage of a pipeline in AWS CodePipeline. AWS CodePipeline is a continuous delivery service that can model, visualize, and automate the steps required to release the code, including building the code.
A pipeline is a workflow construct that describes how code changes go through a release process. See the illustration below:
What are some tools that integrate with AWS CodeBuild and AWS CodePipeline?
Some of the tools that integrate with AWS CodeBuild include; GitHub, GitHub Enterprise, Jenkins, Bitbucket, AWS CodeCommit, AWS CodeFormation, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Amazon S3.
On the other hand, some of the tools that integrate with AWS CodePipeline include; GitHub, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, Jenkins, Cloudbees, and Runscope.
Alternatives to AWS CodeBuild and AWS CodePipeline
Jenkins
Jenkins is the leading open-source continuous integration server. Built with Java, it provides over 300 plugins to support building and testing virtually any project.
AWS CodeDeploy
AWS CodeDeploy is a service that automates code deployments to Amazon EC2 instances. It makes it easier to release new features rapidly, helps avoid downtime during deployment, and handles the complexity of updating applications.
It provides a unified user interface that enables one to easily manage software development activities in one place.
Apache Maven
Maven allows a project to build using its project object model (POM) and a set of plugins that are shared by all projects using Maven, providing a uniform build system.
GitLab CI
GitLab offers a continuous integration service. If a .gitlab-ci.yml file is added to the repository’s root directory, and a GitLab project is configured to use a Runner, then each merge request or push triggers the CI pipeline.
Conclusion
Every project has its own requirements, and every CI/CD is unique. But when such great and easy-to-use tools are available, one might as well want to make smarter use of them.
AWS CodeBuild and AWS CodePipeline protect the secrets, automates jobs, reduce chances of error, and save time and effort. In a poll by Stackshare in its community, “Pay per minute” is the primary reason developers consider AWS CodeBuild over the competitors, whereas “Simple to set up” was stated as the key factor in picking AWS CodePipeline.
Image Credits: stackshare.io
Article Credits: Adit Modi
Cloud Engineer at Digital Alpha | 9x AWS | AWS Community Builder | HashiCorp Ambassador